Can you name the most common skin irritant? Your mind may go
to chemicals like solvents, paint thinners and harsh detergents, but the
answer, surprisingly, is water.
You would not think something as harmless or necessary as water
could cause your skin to become red, dry, itchy and cracked. But that’s exactly
what can happen when your work involves frequent hand washing or immersion in
water.
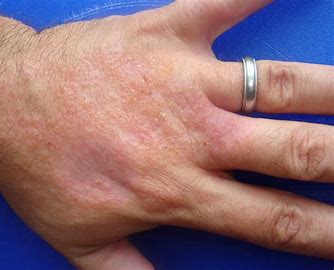
If you perform “wet work” you are most at risk of
occupational contact dermatitis (OCD). OCD is inflammation of the skin caused
by contact with external substances in the workplace. It is one of the most
commonly reported and underestimated occupational diseases.
As well as water, other occupational irritants include any
strongly acidic or alkaline substances, oils, detergents, shampoos, cleaning
agents, dust and fibreglass.
Why is water damaging?
Wetting and drying your hands over and over disrupts the
skin’s key protective layer (the stratum corneum). Over time, this leads to dry
skin, more disruption of the protective barrier, and inflammation.
Frequent contact with water explains in part why people in
the healthcare industry are at greater risk of OCD, as well as hairdressers,
hospitality workers, cleaners and mechanics. And with handwashing more frequent
during the COVID-19 pandemic, more people may be affected.
Your work is considered “wet work” if your hands are:
- in water for longer than two hours a shift
- handling wet things for more than two hours a shift
- in occlusive (moisture-proof) gloves for longer than two hours a shift, or
- washed more than 20 times a shift.
How do you prevent occupational dermatitis?
Gloves. Gloves can protect your hands, but it’s
important to use the right ones for the job as otherwise they may provide inadequate
protection or further irritate your skin.
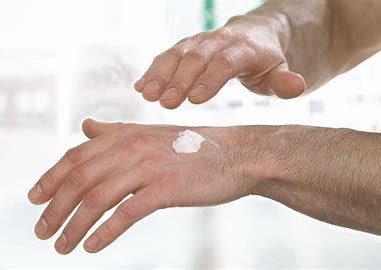
Moisturising creams. These can help prevent dry skin
and dermatitis. Water-based moisturisers may be a better choice, as oil-based
ones can affect the protective properties of certain gloves.
Hand sanitiser. Alcohol-based hand rubs prevent hands
being continually washed and dried and tend to be gentler on the skin, although
they are not suitable if your hands are visibly dirty.
If you have any red, dry and itchy areas on your skin, seek
help from your doctor or dermatologist.